What Is a Microgrid and How Does It Work?
Discover how microgrids integrate solar generation, storage, and control systems to provide resilient, sustainable, and efficient energy for communities and businesses in Chile.

Co-Founder AHORRO ENERGÍA & IoT-MONITOR
What Is a Microgrid?
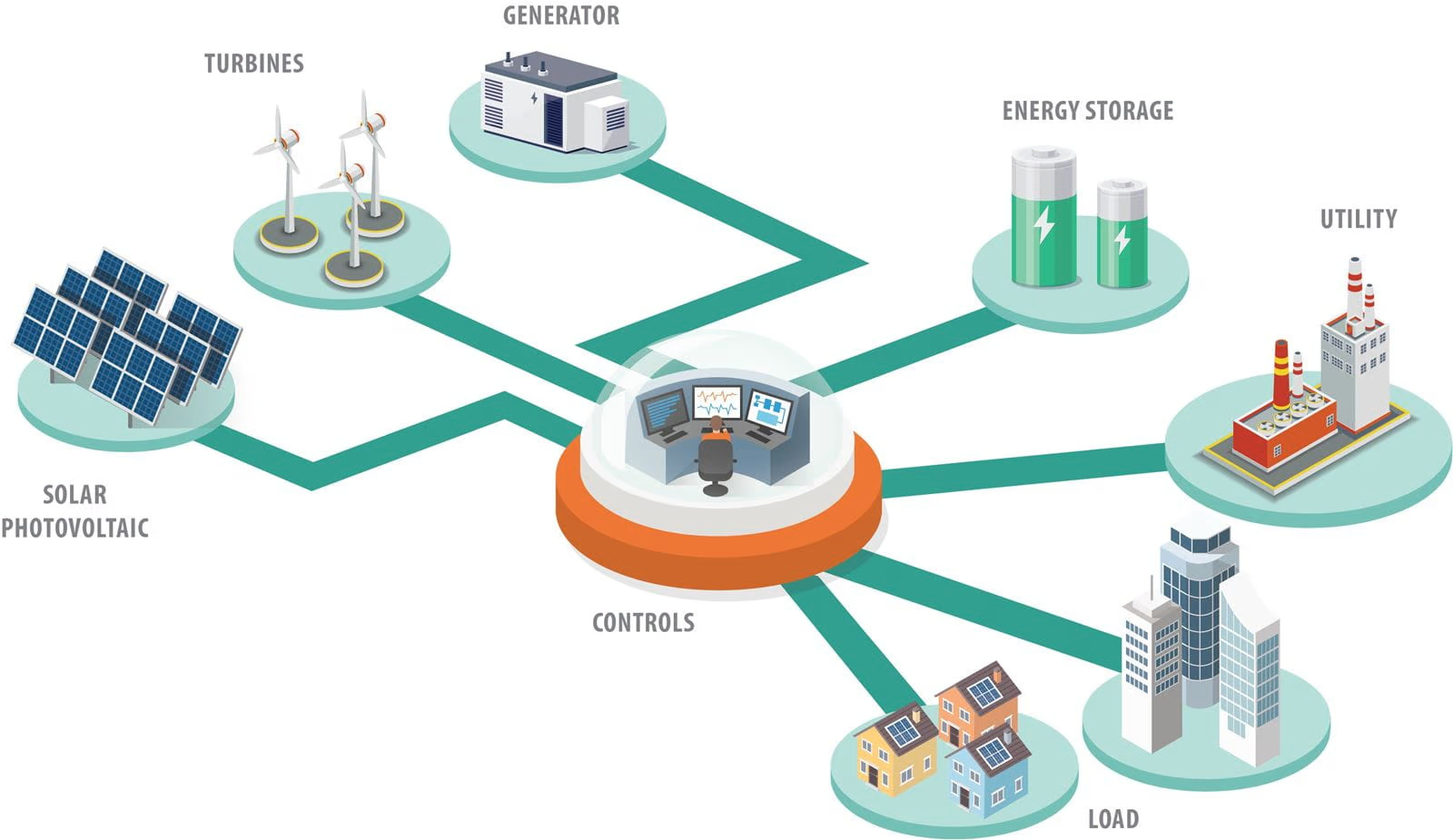
A microgrid is a decentralized electrical system that integrates different energy generation sources, storage, and control systems. Designed to operate independently or connected to the main electrical grid, microgrids represent an efficient and sustainable energy solution that is transforming how communities and businesses access electricity.
These solutions have gained great relevance thanks to their ability to provide resilience against supply interruptions, reduce energy costs, and minimize environmental impact. Microgrids function by combining various technologies, such as solar generators, storage batteries, and intelligent energy management systems.
In the context of solar energy, these installations harness sunlight through photovoltaic panels to generate electricity, which can be stored in batteries and used according to user needs. This approach ensures a continuous and reliable supply, even in the absence of connection to the main grid. Additionally, microgrids enable an effective transition toward a renewable and decentralized energy model, reducing dependence on unsustainable sources.
Essential Components of a Microgrid
The efficient operation of a microgrid requires the integration of several key components that work in harmony to guarantee a reliable and sustainable electrical supply.
Distributed Generation Systems: Distributed generation systems play a central role in microgrids. Photovoltaic solar plants capture solar energy and convert it into electricity, providing a clean and abundant source. Additionally, microgrids can integrate other renewable energy sources such as wind turbines to harness wind energy, and small-scale hydroelectric systems to utilize local water resources. To guarantee operational continuity, diesel generators (genset) can also be incorporated as backup, which activate automatically when renewable sources cannot meet demand or during maintenance periods. This combination of energy sources allows meeting both residential and industrial needs with high reliability.
Energy Storage System: A fundamental element in a microgrid is the energy storage system, which generally uses lithium batteries. These batteries allow storing excess energy generated during the day for use at night or during periods of low solar irradiation. This significantly improves system stability and reliability, ensuring that energy is available when most needed. Additionally, storage systems also help balance generation and consumption, optimizing microgrid performance.
Control and Monitoring System: Another essential component is the control and monitoring system, which uses advanced technologies to monitor energy generation in real time, detect failures, and adjust electrical flow according to demand conditions. The ability to manage energy intelligently not only improves operational efficiency but also reduces maintenance costs and extends equipment lifespan.
Inverters and Conversion Equipment: Inverters are fundamental for converting direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by most equipment. Modern inverters with multiple maximum power point tracking (MPPT) points optimize energy production even in challenging conditions such as partial shading.
Role of Solar Energy in Microgrids
The integration of solar energy in microgrids is one of the most effective strategies for promoting sustainability and energy self-sufficiency. Solar plants are one of the main generation sources in microgrids, providing clean and renewable energy that can meet a wide range of energy needs.
The use of solar panels not only reduces carbon emissions but also decreases long-term operating costs, making them a viable option for communities and businesses. In remote areas or without reliable access to the electrical grid, solar microgrids have proven to be a transformative solution.
By combining solar generation with storage systems, these microgrids can offer a constant and reliable supply, even in adverse conditions. Additionally, advanced technologies such as bifacial panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and solar trackers, which maximize energy capture by adjusting panel orientation, are significantly increasing the efficiency of solar plants in microgrids.
Technological Trends in Solar Microgrids
Microgrids are evolving rapidly thanks to technological advances that improve their efficiency and functionality. One of the most notable trends is the digitization and automation of management systems. Intelligent sensors and remote monitoring platforms allow identifying and resolving problems proactively, reducing downtime and improving installation security.
The use of artificial intelligence facilitates energy flow optimization, ensuring a perfect balance between generation and consumption. Another relevant trend is the development of intelligent inverters that include multiple maximum power point tracking (MPPT) points, optimizing energy production in challenging conditions.
Solar microgrids are also adopting new configurations, such as floating solar plants, which harness water surfaces to generate electricity. This approach not only maximizes the use of available land but also improves panel efficiency by keeping them cool thanks to water. Additionally, integration with smart electrical grids allows optimizing energy flow and minimizing distribution losses.
Practical Applications of Microgrids
Solar microgrids have a wide range of applications that benefit both communities and industries.
Industrial Applications: In the industrial sector, these solutions are used to guarantee reliable electrical supply in manufacturing plants and other critical installations. The ability to operate independently from the main grid ensures operational continuity even during supply interruptions.
Rural and Remote Communities: In rural or remote communities, solar microgrids have transformed the lives of thousands of people by providing access to clean and reliable electricity. These systems allow communities to develop productive activities, improve quality of life, and reduce their dependence on diesel generators, which are expensive and polluting.
Success Cases in Chile: In southern Chile, isolated microgrids have been successfully implemented that combine small-scale hydroelectric energy with photovoltaic energy and lithium batteries. These hybrid solutions demonstrate the versatility of microgrids to adapt to different local energy resources, providing reliable supply in areas where connection to the main grid is not viable.
Critical Infrastructure: Microgrids are also being implemented to protect critical infrastructure such as hospitals, data centers, potable water systems, and telecommunications, ensuring operational continuity in the face of any interruption to the main electrical supply.
Challenges and Solutions in Microgrid Design
Despite their numerous benefits, microgrids face certain technical and regulatory challenges that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Balance between Generation and Consumption: One of the main challenges is ensuring an adequate balance between energy generation and consumption, especially in systems with high penetration of renewable sources. To address this problem, advanced energy management algorithms are being developed that optimize the use of available resources and predict consumption patterns.
Backup Systems: Another challenge is the integration of backup systems that ensure continuous supply in case of generation failures. Technologies such as advanced storage systems with lithium batteries and backup generators are playing a key role in overcoming this obstacle.
Regulatory Framework: Clear regulations and incentives for microgrid adoption are fundamental to fostering their development and expansion. In Chile, the regulatory framework is evolving to facilitate the integration of both connected and isolated microgrids, promoting distributed generation and the energy transition.
Future of Microgrids in Chile and Their Impact on Energy Transition
The future of solar microgrids in Chile is promising, as these solutions continue to demonstrate their ability to accelerate the transition toward a more sustainable energy model. With advances in storage and distributed management technologies, microgrids are becoming a key piece for integrating renewable sources and decentralizing energy generation.
In remote communities, microgrids offer a viable solution for electrifying areas without access to the main grid and closing electricity access gaps. Additionally, their implementation in urban areas of Chile can relieve pressure on main grids, improving supply quality and reducing energy losses.
As technologies continue to evolve, microgrids in Chile will continue to play a fundamental role in building a cleaner and more resilient energy future. Their ability to combine multiple renewable energy sources, intelligent storage, and advanced management makes them a strategic solution for facing the energy challenges of the 21st century.
Why Choose AHORRO-ENERGÍA SpA for Your Microgrid?
With extensive experience in designing and implementing energy systems in Chile, AHORRO-ENERGÍA SpA offers completely customized microgrid solutions that integrate solar generation, storage with lithium batteries, and intelligent energy management systems.
Our microgrid systems are designed to provide resilience, efficiency, and sustainability, adapting to the specific needs of each project, whether for rural communities, industrial installations, or critical infrastructure.
From initial design to continuous operation and maintenance, we guarantee that your microgrid functions optimally, maximizing the use of renewable energies and minimizing operating costs. Contact us and discover how a microgrid can transform your energy access.